A nebulizer is a medical device that converts liquid medication into a fine mist or aerosol that can be inhaled into the lungs. It is commonly used to deliver medication to people with respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, and other lung diseases. Nebulizers are especially useful for patients who have difficulty using inhalers or for those who need large doses of medication.
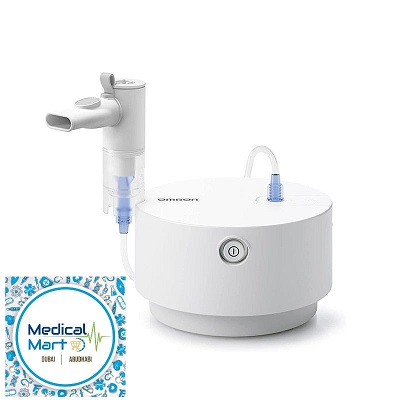
Here’s a general guide on how to use a nebulizer to take care of a patient at home
Gather Supplies:
Nebulizer machine with tubing and mask or mouthpiece.
Medication prescribed by the doctor.
Compressor (the machine that converts the medication into mist).
Clean, dry hands.
A clean work surface.
Distilled water (if required for the specific nebulizer model).
Prepare the Medication:
Wash your hands thoroughly.
Place the medication in the nebulizer cup according to the doctor’s instructions.
If the medication is in liquid form, it can typically be poured directly into the cup. If it’s in a vial, you may need to open it and transfer the solution to the cup.
Assemble the Nebulizer:
Connect the tubing to the nebulizer cup and the compressor.
Attach the mask or mouthpiece to the top of the cup.
Position the Patient:
Have the patient sit upright in a comfortable position.
Encourage them to take slow, deep breaths.
Start the Nebulizer:
Plug in the nebulizer and turn it on.
The machine will start converting the medication into a mist.
Encourage the patient to breathe in and out through the mask or mouthpiece.
Continue the treatment until all the medication in the cup is gone, which typically takes about 10-15 minutes.
Clean and Store:
Turn off the nebulizer and unplug it.
Disassemble the nebulizer and rinse the cup, mask, and tubing with warm water.
Allow the parts to air dry on a clean towel or paper towel.
Store the nebulizer and its components in a clean, dry place.
Follow the Doctor’s Instructions:
Follow the specific instructions provided by the doctor regarding the frequency and dosage of nebulizer treatments.
Monitor for Effectiveness:
Keep an eye on the patient for signs of improvement or worsening of their condition.
Report any concerns or adverse reactions to the doctor.