A defibrillator is a medical device used to deliver an electrical shock to the heart in order to restore normal heart rhythm. It is primarily used in cases of cardiac arrhythmias, where the heart is beating irregularly or too fast (tachycardia) or too slow (bradycardia). Defibrillators are commonly used in emergency situations such as cardiac arrest, where the heart has stopped beating effectively.
The electrical shock delivered by a defibrillator interrupts the chaotic electrical activity in the heart and allows the heart’s natural pacemaker to reestablish a normal rhythm. This process is called defibrillation. Defibrillators can be found in various settings, including hospitals, ambulances, and public places like airports and shopping malls. Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs) are portable devices that are often available in public areas and can be used by non-medical personnel in emergency situations.

Here’s a general overview of how to use a defibrillator at home:
1. Call Emergency Services: If someone is experiencing sudden cardiac arrest, the first step is to call emergency services ( immediately. Time is critical in these situations.
2. Retrieve the AED: If you have an AED at home, retrieve it as quickly as possible. AEDs are often stored in easily accessible locations, such as cabinets or mounted on walls.
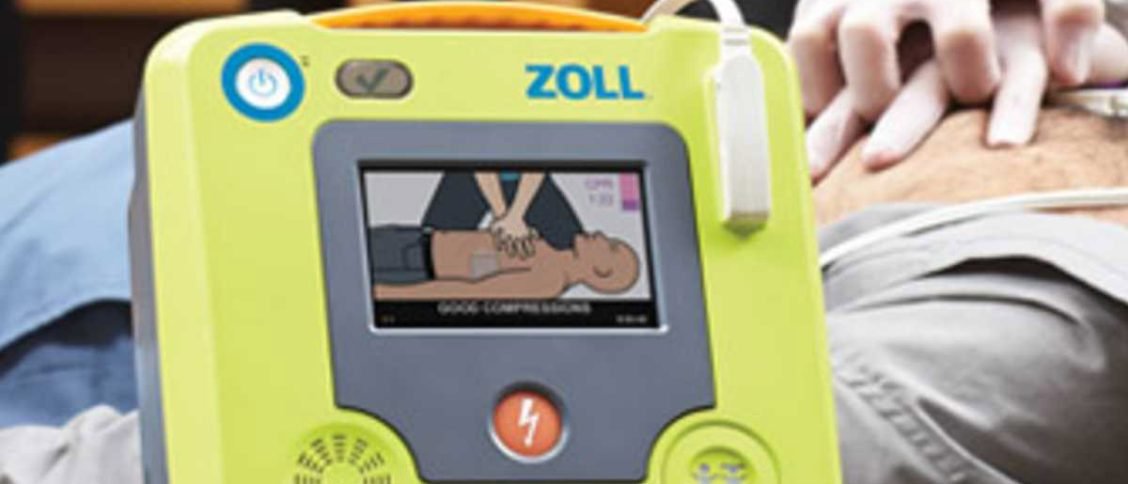
3. Turn On the AED: Most AEDs have an “on” button or switch. Turn on the device to begin the process.
4. Follow Voice and Visual Prompts: AEDs typically provide clear voice and visual prompts to guide users through the process. Follow these prompts carefully. They will instruct you to attach the electrode pads to the person’s chest.
5. Attach Electrode Pads: Remove the clothing from the person’s chest and attach the electrode pads as directed by the AED. Usually, one pad is placed on the upper right chest and the other pad on the lower left side of the chest.
6. Stay Clear During Analysis: Once the electrode pads are attached, the AED will analyze the person’s heart rhythm to determine if a shock is needed. Make sure no one is touching the person during this analysis.
7. Deliver Shock if Advised: If the AED determines that a shock is necessary, it will provide clear instructions to deliver the shock. Make sure everyone is clear of the person before pressing the shock button.
8. Perform CPR: After delivering the shock, the AED may instruct you to perform CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) until emergency medical help arrives. Follow the AED’s instructions for CPR, if needed.
Continue to Follow Instructions: Throughout the process, continue to follow the AED’s voice and visual prompts until emergency medical help arrives.